The effect of Mefenamic Acid on oxidative stress status in male Wistar rats’ model of the seizures
کد: G-1038
نویسندگان: Fateme Meraji ℗, Hasan Rajabi Maham ©, Abdolkarim Hosseini, Vahid Azizi
زمان بندی: زمان بندی نشده!
دانلود: دانلود پوستر
خلاصه مقاله:
background
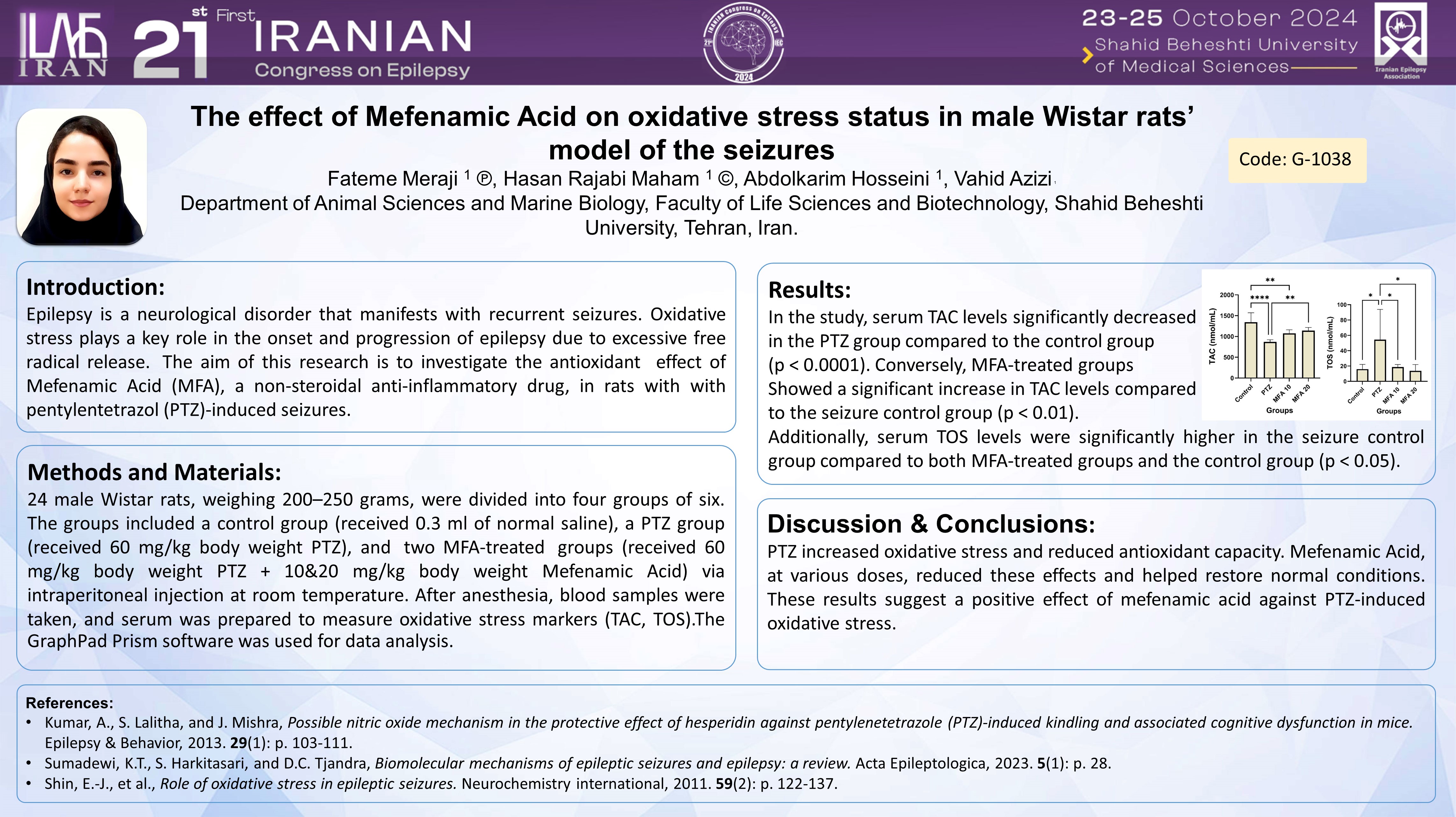
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that manifests with recurrent seizures. Oxidative stress plays a key role in the onset and progression of epilepsy due to excessive free radical release. The aim of this research is to investigate the effect of antioxidant drugs, including Mefenamic Acid (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug - NSAID), in alleviation of seizures.
Methods
24 male Wistar rats, weighing 200–250 grams, were divided into four groups of six. The groups included a control group (received 0.3 ml of normal saline), a control seizure group (received 60 mg/kg body weight PTZ), and two MFA-treated groups (received 60 mg/kg body weight PTZ + 10&20 mg/kg body weight Mefenamic Acid) via intraperitoneal injection at room temperature. After anesthesia, blood samples were taken, and serum was prepared to measure oxidative stress markers (TAC, TOS).The GraphPad Prism software was used for data analysis.
Findings
In the study, serum TAC levels significantly decreased in the seizure control group compared to the control group (p 0.0001). Conversely, MFA-treated groups showed a significant increase in TAC levels compared to the seizure control group (p 0.01). Additionally, serum TOS levels were significantly higher in the seizure control group compared to both MFA-treated groups and the control group (p 0.05).
Conclusion
PTZ increased oxidative stress and reduced antioxidant capacity. Mefenamic acid, at various doses, reduced these effects and helped restore normal conditions. These results suggest a positive effect of mefenamic acid against PTZ-induced oxidative stress.
Key words
Seizures; Mefenamic-Acid; Oxidative-stress